SI Units (système international)
The SI system identifies base units
These are defined very precisely and are independent of one another
Each is appropriate to a different type of quantity
These types of quantity are sometimes called dimensions
Base units used in Chemistry
quantity |
unit |
mass |
kg |
length |
m |
time |
s |
electrical current |
A |
temperature |
K |
amount |
mol |
Derived units
All other SI units can be expressed in terms of base units
It is easy to do this if you know a definition of some form of the quantity
For example energy (J), using the definition of kinetic energy:
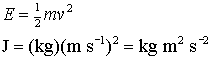
Of course you have to know the units of mass (kg) and speed (m s-1)
The factor of ½ is a pure number and does not affect the units.